FIGS (Quick Interpretable Grasping-tree Sums): A way for constructing interpretable fashions by concurrently rising an ensemble of determination bushes in competitors with each other.
Current machine-learning advances have led to more and more complicated predictive fashions, typically at the price of interpretability. We frequently want interpretability, notably in high-stakes functions corresponding to in scientific decision-making; interpretable fashions assist with all types of issues, corresponding to figuring out errors, leveraging area data, and making speedy predictions.
On this weblog put up we’ll cowl FIGS, a brand new methodology for becoming an interpretable mannequin that takes the type of a sum of bushes. Actual-world experiments and theoretical outcomes present that FIGS can successfully adapt to a variety of construction in information, reaching state-of-the-art efficiency in a number of settings, all with out sacrificing interpretability.
How does FIGS work?
Intuitively, FIGS works by extending CART, a typical grasping algorithm for rising a call tree, to think about rising a sum of bushes concurrently (see Fig 1). At every iteration, FIGS could develop any current tree it has already began or begin a brand new tree; it greedily selects whichever rule reduces the full unexplained variance (or another splitting criterion) essentially the most. To maintain the bushes in sync with each other, every tree is made to foretell the residuals remaining after summing the predictions of all different bushes (see the paper for extra particulars).
FIGS is intuitively much like ensemble approaches corresponding to gradient boosting / random forest, however importantly since all bushes are grown to compete with one another the mannequin can adapt extra to the underlying construction within the information. The variety of bushes and dimension/form of every tree emerge routinely from the info reasonably than being manually specified.
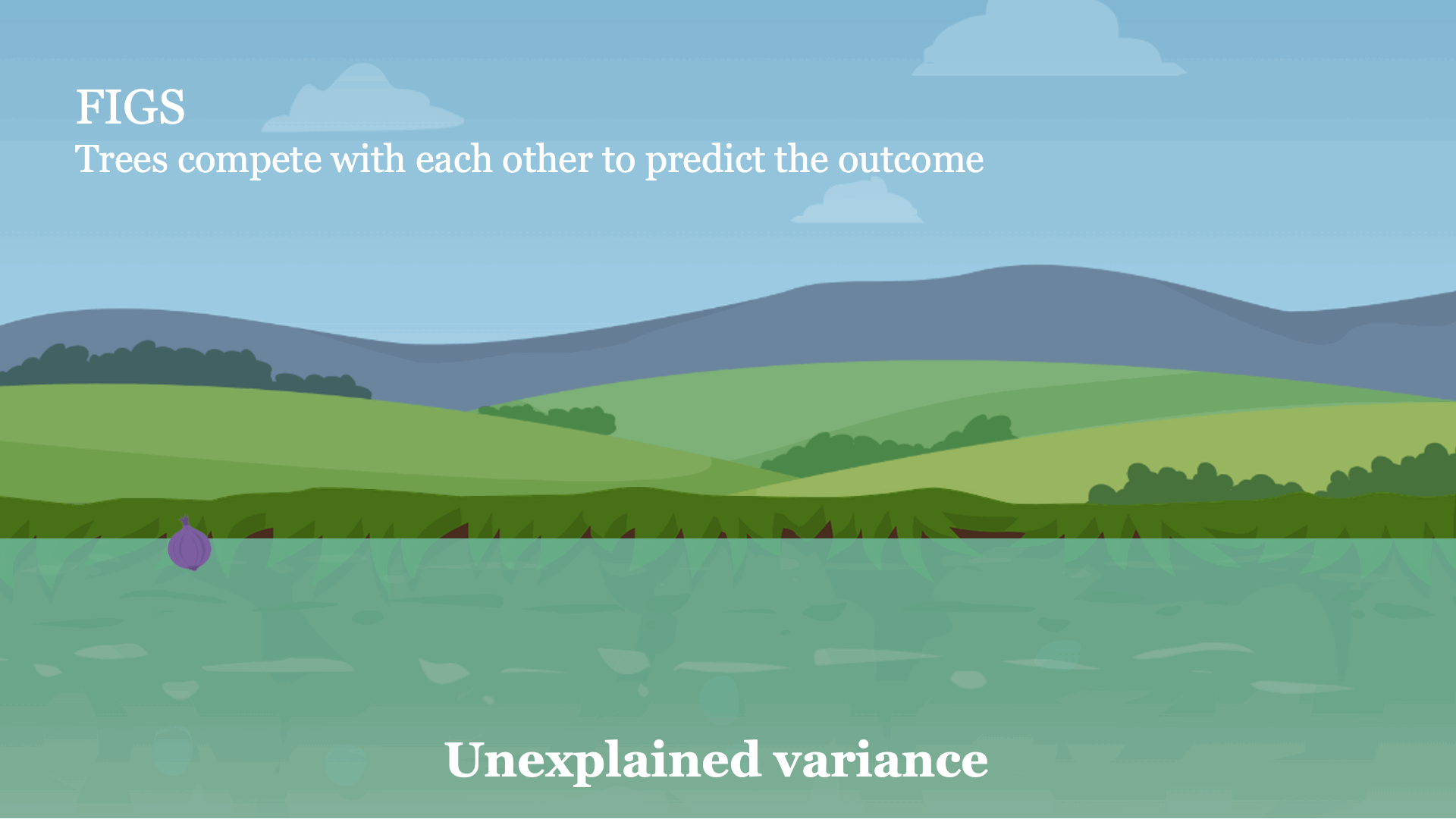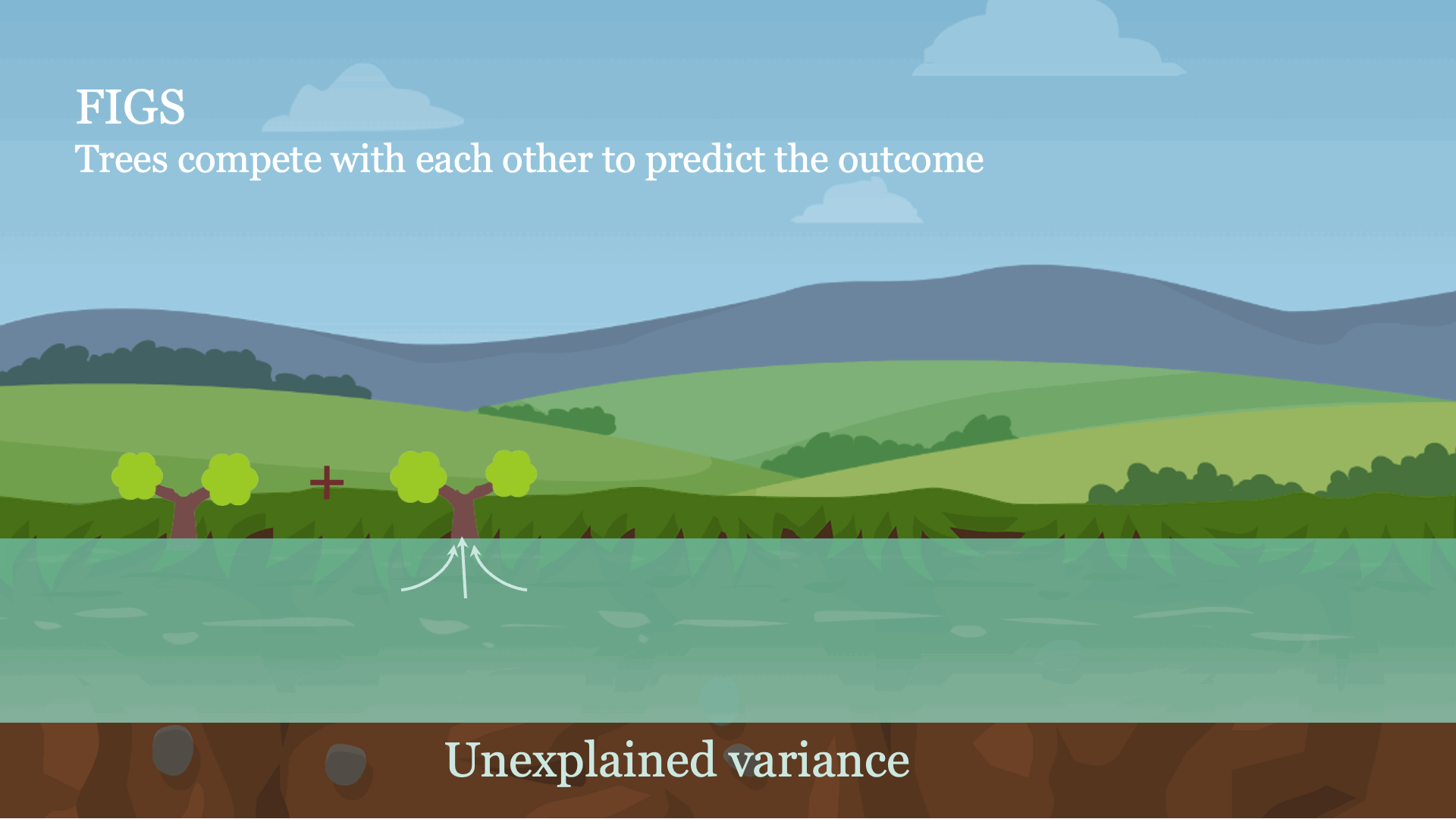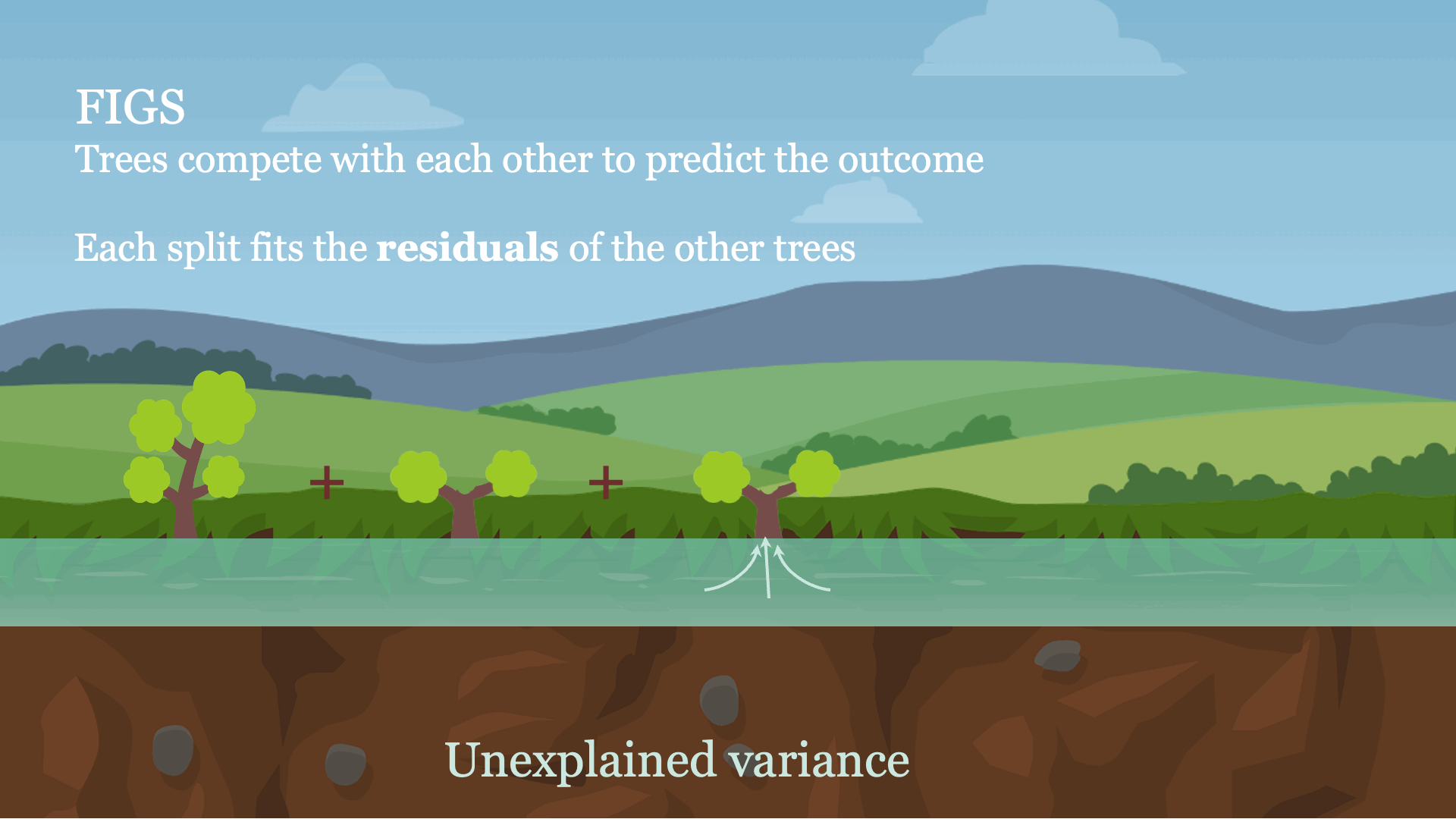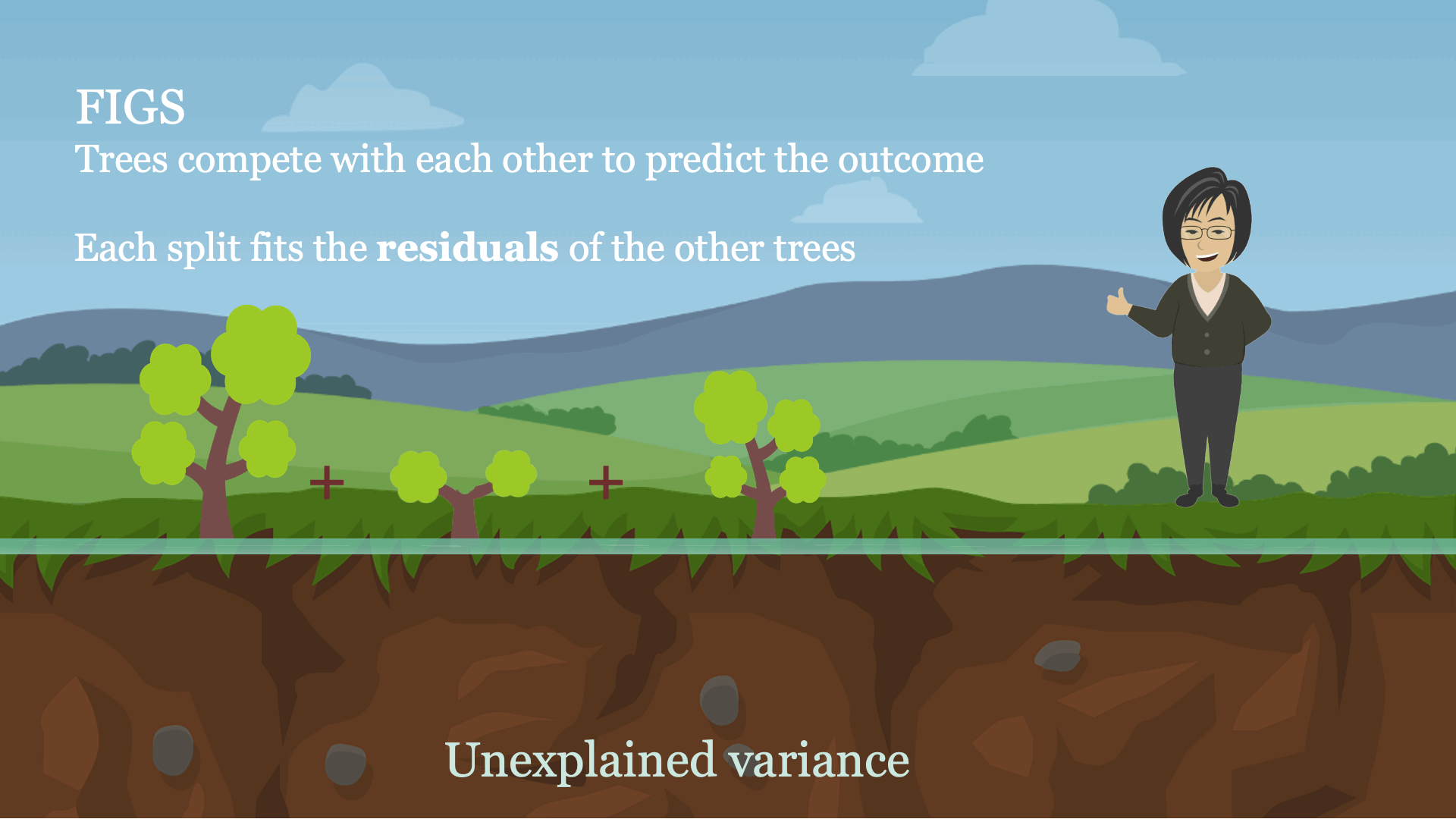
Fig 1. Excessive-level instinct for a way FIGS matches a mannequin.
An instance utilizing FIGS
Utilizing FIGS is very simple. It’s simply installable by way of the imodels package deal (pip set up imodels) after which can be utilized in the identical manner as normal scikit-learn fashions: merely import a classifier or regressor and use the match and predict strategies. Right here’s a full instance of utilizing it on a pattern scientific dataset during which the goal is threat of cervical backbone harm (CSI).
from imodels import FIGSClassifier, get_clean_dataset
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# put together information (on this a pattern scientific dataset)
X, y, feat_names = get_clean_dataset('csi_pecarn_pred')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
# match the mannequin
mannequin = FIGSClassifier(max_rules=4) # initialize a mannequin
mannequin.match(X_train, y_train) # match mannequin
preds = mannequin.predict(X_test) # discrete predictions: form is (n_test, 1)
preds_proba = mannequin.predict_proba(X_test) # predicted possibilities: form is (n_test, n_classes)
# visualize the mannequin
mannequin.plot(feature_names=feat_names, filename='out.svg', dpi=300)
This leads to a easy mannequin – it comprises solely 4 splits (since we specified that the mannequin should not have any greater than 4 splits (max_rules=4). Predictions are made by dropping a pattern down each tree, and summing the danger adjustment values obtained from the ensuing leaves of every tree. This mannequin is extraordinarily interpretable, as a doctor can now (i) simply make predictions utilizing the 4 related options and (ii) vet the mannequin to make sure it matches their area experience. Be aware that this mannequin is only for illustration functions, and achieves ~84% accuracy.
Fig 2. Easy mannequin discovered by FIGS for predicting threat of cervical spinal harm.
If we wish a extra versatile mannequin, we are able to additionally take away the constraint on the variety of guidelines (altering the code to mannequin = FIGSClassifier()), leading to a bigger mannequin (see Fig 3). Be aware that the variety of bushes and the way balanced they’re emerges from the construction of the info – solely the full variety of guidelines could also be specified.
Fig 3. Barely bigger mannequin discovered by FIGS for predicting threat of cervical spinal harm.
How effectively does FIGS carry out?
In lots of circumstances when interpretability is desired, corresponding to clinical-decision-rule modeling, FIGS is ready to obtain state-of-the-art efficiency. For instance, Fig 4 reveals totally different datasets the place FIGS achieves wonderful efficiency, notably when restricted to utilizing only a few complete splits.
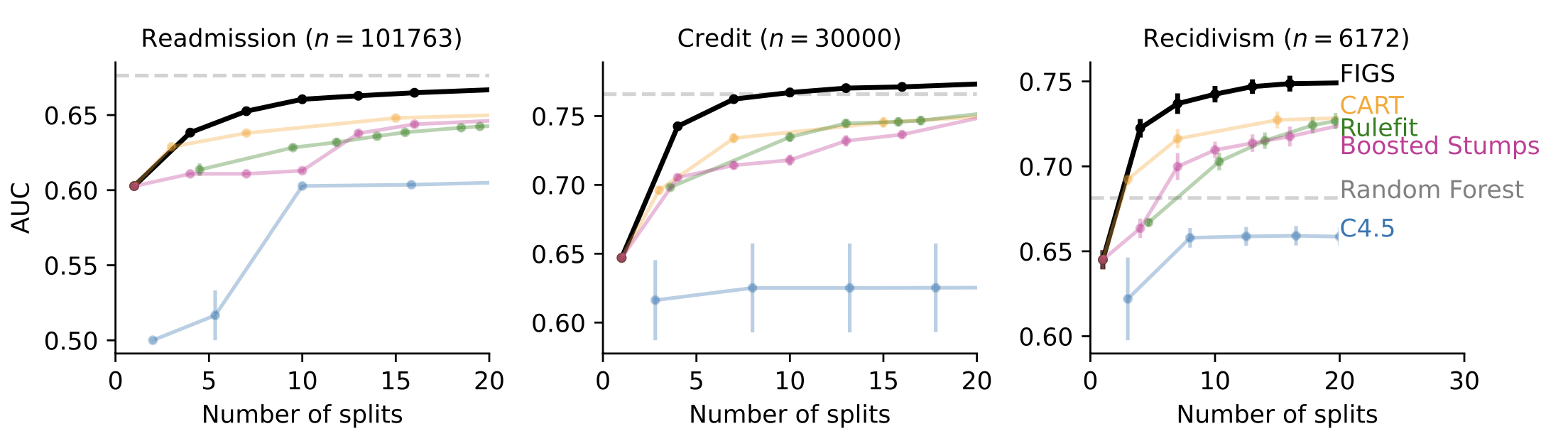
Fig 4. FIGS predicts effectively with only a few splits.
Why does FIGS carry out effectively?
FIGS is motivated by the remark that single determination bushes typically have splits which are repeated in several branches, which can happen when there’s additive construction within the information. Having a number of bushes helps to keep away from this by disentangling the additive elements into separate bushes.
Conclusion
Total, interpretable modeling provides a substitute for widespread black-box modeling, and in lots of circumstances can supply large enhancements when it comes to effectivity and transparency with out affected by a loss in efficiency.
This put up relies on two papers: FIGS and G-FIGS – all code is on the market by way of the imodels package deal. That is joint work with Keyan Nasseri, Abhineet Agarwal, James Duncan, Omer Ronen, and Aaron Kornblith.